How to operate a drone safely and effectively is more than just mastering the controls; it’s about understanding the technology, adhering to regulations, and appreciating the art of aerial photography and videography. This guide delves into the essential aspects of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to mastering flight maneuvers and optimizing image quality. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone controls, battery management, and maintenance, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly and creatively.
We’ll cover everything from understanding your drone’s functionalities and navigating various flight modes to optimizing your camera settings for stunning aerial shots. Learn how to plan captivating flight paths, troubleshoot common issues, and ensure the longevity of your drone through proper maintenance. This comprehensive guide aims to transform you from a novice into a skilled and responsible drone pilot.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s physical condition, verifying system functionality, and confirming compliance with local regulations. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents and legal repercussions.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection involves systematically checking various aspects of the drone to ensure it’s in optimal flying condition. This includes verifying the integrity of its components, checking battery levels, and confirming proper functionality of its systems.
| Item | Check | Action Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for cracks, damage, or imbalance. | Replace damaged propellers. Ensure all propellers are securely fastened. | Check for proper alignment and tightness. |
| Battery | Check battery level and condition. | Charge battery to full capacity if necessary. Replace damaged or swollen batteries. | Avoid using damaged or low-quality batteries. |
| Gimbal | Check for smooth movement and proper functionality. | Adjust or calibrate gimbal if necessary. | Ensure the gimbal is securely mounted. |
| Camera | Check lens for smudges or damage. | Clean lens with a microfiber cloth. | Ensure the camera is securely mounted and functioning correctly. |
| Sensors | Verify that all sensors (GPS, IMU, etc.) are functioning correctly. | Calibrate sensors if necessary. Consult the drone’s manual for calibration procedures. | Ensure sensors are clean and unobstructed. |
| Radio Control System | Check the connection between the remote and the drone. | Ensure the batteries in the remote controller are charged and functioning. | Test all controls on the remote to ensure proper response. |
Understanding Local Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Operating a drone requires understanding and adhering to local laws and regulations. These rules vary by location and often involve restrictions on flight altitude, proximity to airports, and designated no-fly zones. Ignorance of these regulations can lead to hefty fines, drone confiscation, or even criminal charges.
For example, flying near airports without proper authorization is a serious offense that can result in significant penalties. Similarly, flying over private property without permission can lead to legal action. Always check the local regulations and obtain necessary permits before flying.
Safe Drone Launch and Landing Procedure

A clear sequence of actions is essential for safe drone launches and landings. This flowchart illustrates a step-by-step process to minimize risks.
(A visual flowchart would be included here, depicting steps such as pre-flight checks, selecting a safe location, powering on the drone and controller, calibrating the compass and GPS, performing a test hover, initiating takeoff, executing the flight, and performing a safe landing. The flowchart would visually represent the sequence of actions using boxes, arrows, and decision points.)
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to respond to emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. This includes situations like malfunctioning components or signal loss.
- Malfunctioning Drone: If the drone malfunctions, attempt to initiate a return-to-home (RTH) function if available. If RTH fails, try to regain control manually. If control cannot be regained, attempt to guide the drone to a safe landing area, avoiding populated areas or obstacles.
- Signal Loss: If the signal is lost, the drone will typically attempt to return to its home point (if this function is enabled). If the RTH fails, the drone may enter a failsafe mode and land automatically, depending on the drone’s capabilities and settings. Keep a visual on the drone as much as possible.
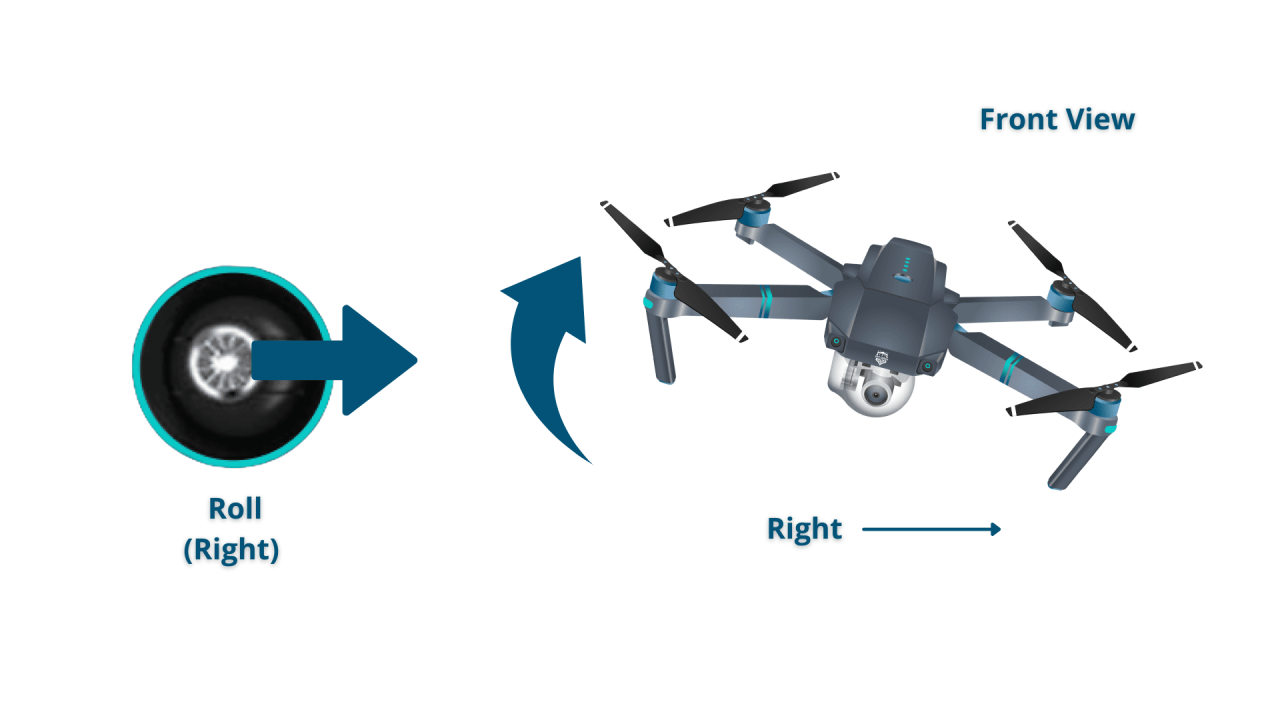
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section covers calibration, maneuvering techniques, flight modes, and control functions.
Drone Compass and GPS Calibration
Accurate compass and GPS calibration are essential for precise drone navigation and stability. These steps ensure that the drone understands its location and orientation correctly.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Ensure the drone is in an open area, away from magnetic interference (e.g., metal objects, power lines).
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for compass calibration. This typically involves rotating the drone slowly in a figure-eight pattern.
- Allow the GPS to acquire a sufficient number of satellites (usually indicated by the drone’s software). This can take several minutes.
- Once calibration is complete, verify the accuracy of the compass and GPS readings using the drone’s software.
Maneuvering in Various Wind Conditions
Wind significantly affects drone flight, requiring adjustments to control inputs. Experience and understanding are key to maintaining stability in windy conditions.
- Light Wind: Minor adjustments to control inputs are usually sufficient.
- Moderate Wind: Maintain a stable flight attitude by making gradual corrections. Avoid abrupt movements.
- Strong Wind: Consider landing the drone or adjusting the flight plan to minimize exposure to strong winds. It may be necessary to increase the drone’s throttle to maintain altitude.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of stability and control. Understanding their purpose is crucial for safe and effective operation.
| Flight Mode | Description | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| GPS Mode | Maintains position and altitude using GPS data. | Stable flight, ideal for beginners and precise positioning. |
| Attitude Mode | Controls drone attitude (pitch, roll, yaw) relative to its current orientation. | More agile control, suitable for experienced pilots and dynamic maneuvers. |
| Manual Mode | Provides direct control over all aspects of flight. | Requires significant experience and skill. Not recommended for beginners. |
Drone Remote Control Functions
Understanding the functions of each control stick and button is essential for effective drone operation.
| Control | Function |
|---|---|
| Left Stick (Vertical/Horizontal) | Controls altitude and forward/backward movement. |
| Right Stick (Yaw/Lateral) | Controls yaw (rotation) and left/right movement. |
| Buttons | Vary depending on the drone model, but typically include functions like return-to-home (RTH), camera control, and emergency stop. |
Taking High-Quality Aerial Photographs and Videos
Capturing stunning aerial imagery requires understanding camera settings, composition techniques, and smooth flight maneuvers.
Camera Settings Adjustment

Optimizing camera settings is crucial for achieving high-quality images in various lighting conditions. Adjustments should be made based on the specific lighting environment.
- ISO: Lower ISO values (e.g., 100-400) reduce noise but require more light. Higher ISO values (e.g., 800+) increase sensitivity but introduce more noise.
- Shutter Speed: A fast shutter speed freezes motion, while a slow shutter speed can create motion blur. The appropriate shutter speed depends on the subject’s movement and desired effect.
- Aperture: A wide aperture (low f-stop number, e.g., f/2.8) creates a shallow depth of field, blurring the background. A narrow aperture (high f-stop number, e.g., f/16) increases depth of field, keeping both foreground and background sharp.
Aerial Photography Composition Techniques
Effective composition enhances the visual appeal of aerial shots. These techniques guide the viewer’s eye and create compelling images.
- Leading Lines: Use roads, rivers, or other lines to draw the viewer’s eye into the scene.
- Rule of Thirds: Place key elements off-center to create a more balanced and visually appealing composition.
- Symmetry and Patterns: Capture symmetrical scenes or repeating patterns for a visually striking effect.
- Perspective: Use altitude and angle to create unique perspectives that ground-level photography cannot achieve.
- Framing: Use natural elements (trees, buildings) to frame your subject and add depth to the image.
Planning and Executing Smooth Drone Movements
Smooth, cinematic drone movements enhance video quality. Careful planning and execution are crucial for achieving these effects.
- Practice Smooth Movements: Practice slow, deliberate movements to avoid jerky or abrupt changes in camera position.
- Plan Your Shots: Visualize your shots beforehand to ensure smooth transitions and avoid unnecessary movements.
- Use Different Angles: Experiment with different camera angles to create dynamic and engaging footage.
- Vary Your Speed: Vary the drone’s speed to create visual interest and emphasize certain aspects of the scene.
Post-Processing Drone Footage
Post-processing enhances the visual appeal of drone footage. These best practices ensure high-quality results.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires understanding regulations and practicing safe flight procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and ensure you’re prepared for a safe and successful flight.
Proper training is crucial before operating any drone responsibly.
- Color Correction: Adjust color balance and saturation to improve the overall look of the footage.
- Stabilization: Use software to stabilize shaky footage, creating smoother transitions.
- Grading: Apply color grading to create a consistent look and feel across the video.
- Editing: Use video editing software to cut, arrange, and add transitions to create a compelling narrative.
Battery Management and Flight Time Optimization
Proper battery management extends battery lifespan and maximizes flight time. Understanding factors affecting flight time is essential for efficient drone operation.
Proper Charging and Storage of Drone Batteries
Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for charging and storing drone batteries is crucial for maintaining their performance and extending their lifespan. Overcharging or improper storage can damage the batteries and shorten their operational life.
- Charging: Use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow the instructions carefully. Avoid overcharging.
- Storage: Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Store them at a partially charged state (around 30-50%) for long-term storage.
Factors Affecting Flight Time
Several factors influence drone flight time. Understanding these factors helps in planning flights and maximizing flight duration.
- Wind Speed: Stronger winds increase energy consumption, reducing flight time.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures (both hot and cold) can affect battery performance and reduce flight time.
- Payload Weight: Carrying heavier payloads (e.g., larger cameras) increases energy consumption and reduces flight time.
Battery Percentage and Remaining Flight Time
The relationship between battery percentage and remaining flight time varies depending on the drone model and flight conditions. This table provides a sample for a hypothetical drone.
| Battery Percentage (%) | Approximate Remaining Flight Time (minutes) |
|---|---|
| 100 | 25 |
| 80 | 20 |
| 60 | 15 |
| 40 | 10 |
| 20 | 5 |
| 0 | 0 |
Note: This is a hypothetical example. Consult your drone’s manual for accurate flight time estimations.
Maximizing Flight Time
Employing efficient flight patterns and minimizing unnecessary maneuvers extends flight time.
- Efficient Flight Patterns: Plan your flight path to minimize unnecessary turns and maneuvers.
- Minimize Hover Time: Avoid prolonged hovering, as it consumes more battery power.
- Avoid Aggressive Maneuvers: Avoid sudden acceleration or deceleration, which increases energy consumption.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This includes cleaning, inspection, part replacement, and addressing common issues.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule ensures the drone’s longevity and safe operation. This involves cleaning, inspecting, and lubricating components as needed.
- Weekly Inspection: Visually inspect the drone for any damage or loose parts. Clean the propellers and body with a soft cloth.
- Monthly Cleaning: Thoroughly clean the drone body, propellers, and camera lens. Use compressed air to remove dust and debris from sensitive components.
- Quarterly Check: Inspect all moving parts for wear and tear. Lubricate moving parts as needed, following the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Replacing Common Drone Parts
Knowing how to replace common parts, such as propellers, ensures quick repairs and minimizes downtime.
- Carefully remove the damaged propeller.
- Align the new propeller with the motor shaft.
- Securely fasten the new propeller using the appropriate screws.
- Repeat for all damaged propellers.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Addressing common drone issues promptly ensures continued safe operation.
- Low Battery Warning: Land the drone immediately and charge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Relocate to an area with better GPS reception. Ensure that the GPS module is clean and unobstructed.
- Motor Issues: Inspect the motors for damage or obstructions. If a motor is malfunctioning, it may need to be replaced.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Recalibrate the gimbal or check for physical obstructions.
- Remote Controller Issues: Check the batteries in the remote controller and ensure a strong connection between the remote and the drone.
Proper Drone and Accessory Storage, How to operate a drone
Proper storage protects the drone and its accessories from damage. A designated storage case or container is recommended.
(A visual guide would be included here, depicting the proper way to store the drone, including securing propellers, protecting the camera, and organizing accessories in a case or container. The guide would show how to avoid potential damage from impact, dust, and moisture.)
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical skill with creative vision. By understanding the pre-flight procedures, navigating the controls with precision, and optimizing your camera settings, you can capture breathtaking aerial footage and images. Remember that responsible operation is paramount – always adhere to local regulations and prioritize safety. With practice and a commitment to continuous learning, you’ll unlock the full potential of your drone and embark on countless exciting aerial adventures.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, responsible drone operation requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the regulations.
General Inquiries
What is the best drone for beginners?
There are several user-friendly drones on the market ideal for beginners, often featuring intuitive controls and safety features. Research models known for their ease of use and positive user reviews.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass and GPS?
It’s recommended to calibrate your drone’s compass and GPS before each flight, especially if you’re in a new location or have experienced any significant interference.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If it doesn’t work, try to regain signal or manually guide the drone back to a safe landing area.
Can I fly my drone in rain or snow?
No, avoid flying your drone in inclement weather. Moisture can damage the drone’s electronics and compromise its performance and safety.
How do I legally fly a drone?
Register your drone with the relevant aviation authority in your country and always comply with local regulations regarding airspace restrictions and flight limitations.